What Is Gingivectomy?
Gingivectomy is the reduction of gum tissue around the teeth or edentulous ridges. There can be many reasons for a gingivectomy, including:
Esthetics: For patients with excessive gum tissue, a gingivectomy can improve the appearance of the smile. This is often related to conditions like "gummy smile," where the gums cover a significant portion of the teeth. By reshaping the gums, the teeth appear longer and more proportionate.
Access for Oral Hygiene: In cases where gum tissue overgrowth occurs—often due to conditions like gingival hyperplasia—removing the excess tissue can help patients maintain better oral hygiene. Improved access allows for more effective brushing and flossing, which can reduce the risk of further gum disease.
Pocket Reduction: Gingivectomy can be used to treat periodontal disease. By removing diseased gum tissue, the procedure helps reduce the depth of periodontal pockets, making it easier to clean and maintain healthy gums. This can lead to improved overall periodontal health and reduce the risk of tooth loss.
Treatments and Techniques
Laser Gingivectomy: This minimally invasive approach uses laser technology to remove excess gum tissue with precision. The laser minimizes bleeding and promotes faster healing compared to traditional methods.
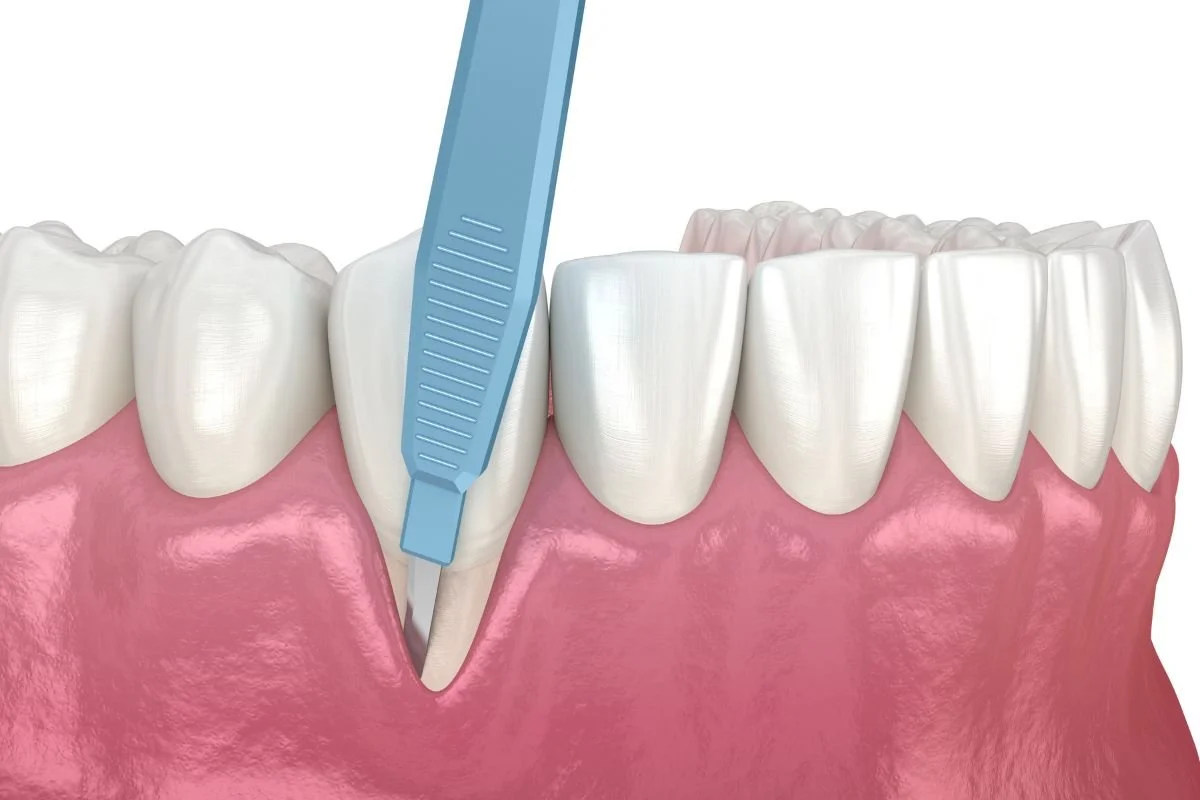
Traditional Surgical Gingivectomy: In this method, a scalpel is used to remove the excess gum tissue. Local anesthesia is typically administered to ensure patient comfort. The surgeon will carefully contour the gums to achieve the desired aesthetic and functional results.
Esthetic Crown Lengthening: This specific type of gingivectomy is performed to expose more of the tooth structure for restorations, such as crowns or veneers. It involves removing gum tissue to allow for proper tooth preparation, enhancing both function and appearance.
Post-Operative Care: Following a gingivectomy, patients may need to follow specific care instructions to ensure proper healing. This can include pain management, maintaining oral hygiene, and avoiding certain foods that could irritate the gums.
Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing and ensure that the gums are responding positively to the treatment. This is also an opportunity for dental professionals to reinforce proper oral hygiene practices.